What You Need to Know About African Clawed Frogs
A Closer Look at the African Clawed Frog
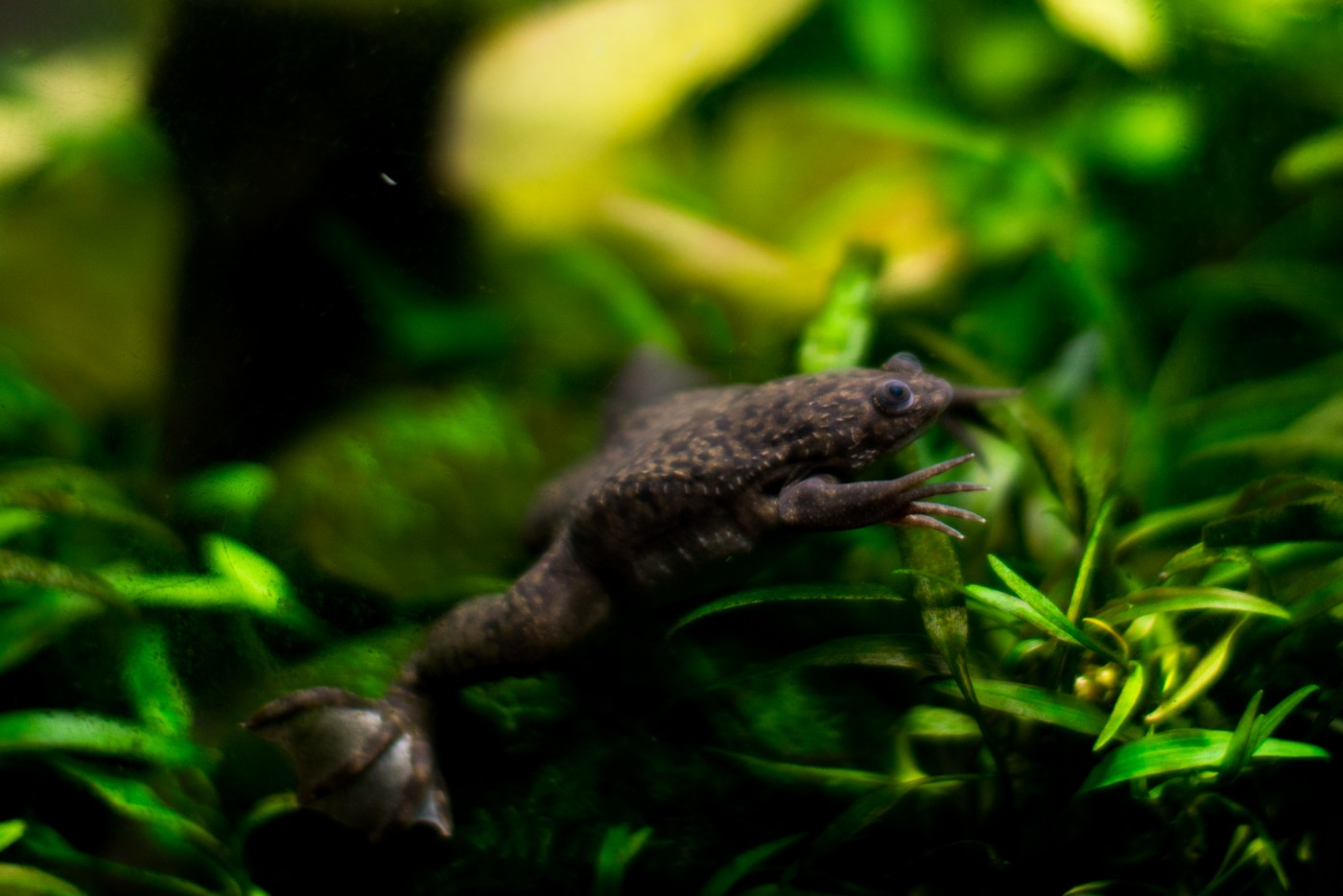
The African clawed frog is a large and colorful frog that lives in the rainforest areas of Western Africa. The African clawed frog, or Xenopus laevis, is a large and colorful frog that lives in the rainforest areas of West Africa. It can grow from 1/2 to 16 inches long, with as many as 80 different color variations! African clawed frogs live in groups and eat small invertebrates such as insects and spiders.
The African clawed frog is a large and colorful frog that lives in the rainforest. areas of Western Africa. The African clawed frog, or Xenopus laevis, is a large and colorful frog that lives in the rainforest areas of West Africa. It can grow from 1/2 to 16 inches long, with as many as 80 different color morphs.
Frogs have been around for more than 350 million years, but they have changed very little over this long period of time.
The African clawed frog is one of the most interesting frogs because it has developed a way to protect its eyes from predators by curling its eyelids into itself.
What Does an African Clawed Frog Look Like?
The African clawed frog is a small frog that has a long, thin body and legs. It has three toes on each foot. This animal is native to Africa and can be found in both wet and dry habitats. The African clawed frog has dark brown or black skin with yellow spots on its back, head, and legs. Its eyes are circular and have yellow sclera, iridescent black pupils, and white flecks on the inside. The frog's body is triangular in shape. The African-clawed frog's head is flat, with a broad snout that has a keratinous protuberance above each nostril that can be moved forward or back for breathing.
How Do African Clawed Frogs Communicate with Each Other?
There are many reasons why these frogs make the sounds they do. One reason is that they use a call to communicate when they are looking for a mate. The sound of a large frog can be heard by smaller frogs and vice versa. This helps them to find each other in the wild without being eaten by predators.
The area where the Giant Golden-crowned Treefrog lives is tropical rainforest. In this environment, the frogs have many predators. This includes birds, snakes, and toads. The frogs have developed some special adaptations to help avoid predators such as sharp spines on their heads and strong claws on their four front feet. As it is a tropical rainforest, the frogs are in a moist environment.
The frogs can use their spines to protect themselves from insects that might bite or sting them. The Giant Golden-crowned Treefrog is not very common and it is on the brink of extinction. It is listed as critically endangered according to the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. It is listed as Critically Endangered because it is estimated that there are less than 10,000 individuals left in the wild. It has been found in a limited area of Ecuador. The male's voice ranges from high-pitched chirps to a low-pitched croak. The female is almost silent and only makes her call when she is Unsafe.
Frogs communicate with each other through mating calls and sounds in order to find mates and avoid predators. Frogs are not slimy slime coats a frog is made up of tiny hairs called setae that cling to the surface.
What Are Some Interesting Facts About the African Clawed Frog?
African Clawed Frogs are an interesting species of frogs that have a sharp, curved claw on their back legs. The African Clawed Frog is the largest frog in the world. It can grow up to 10 inches long and weighs about 4 pounds, is also one of the most endangered species of frogs in the world.
The African Clawed Frog has a large, dark brown head and a long, pale golden brown body. The back of the African Clawed Frog is covered in large orange bumps that look like claws. On each hind leg of the African Clawed Frog, there are three claw-like toes. This species has no webbing between its toes which is unusual for frogs. The African Clawed Frog can be found in most of sub-Saharan Africa. This species is typically found in wetlands, rivers, streams, and ponds. It is rare to find them in saltwater areas.
Conclusion on 3 Things You Need to Know About African Clawed Frogs
African Clawed Frogs are a type of frog which is native to Africa. They are also known as the "Frogs with the Big Feet" because of their large, webbed feet.
1) African Clawed Frogs are a type of frog which is native to Africa. They are also known as the "Frogs with the Big Feet" because of their large, webbed feet.
2) One interesting fact about these frogs is that they can jump up to 3 meters in height and have been known to jump over waterfalls and even crocodiles!
3) The African Clawed Frog has been listed as an endangered species due to habitat loss and extensive hunting for food or for medicinal purposes.